Parsing Excel Files at Scale with Docling

Sep 8, 2025
Executive Summary
Excel is one of the most widely used tools for managing and sharing data. Yet, extracting structured and meaningful information from .xlsx files is often harder than it seems. Our team set out to find a solution that could reliably parse tables and text together, maintain context and formatting, and work without relying on paid APIs or external services.
After exploring several libraries and approaches, we discovered Docling, a solution that balanced flexibility, scalability, and reliability, making it the best fit for our needs.

Challenges
At first glance, parsing Excel sounds straightforward. But when we started working with real-world files, we quickly ran into roadblocks:
- Different table types: Some files used native Excel tables, while others had only simple tabular ranges. Most tools could handle one type but not both.
- Context loss: In many cases, tables were surrounded by important explanatory text. Traditional libraries ignored this, leaving us with incomplete data.
- Table boundaries: Detecting where a table started and ended became tricky, especially when multiple tables existed in the same sheet.
- Maintenance burden: The more logic we added to patch gaps in existing libraries, the more brittle and complex the system became.
- Scalability issues: Our solution had to process thousands of files, not just a handful. Performance and reliability mattered.
These challenges motivated us to step back and rethink our approach.
Motivation
Our motivation was simple but clear:
We wanted to build a robust, free, and local-first tool that could parse Excel files while retaining both tables and context. Specifically, the tool needed to:
- Parse native tables as well as simple tabular ranges.
- Extract tables together with text, not in isolation.
- Preserve formatting and relationships between data and notes.
- Append text alongside tables when needed for clarity.
- Avoid dependency on paid APIs or complex external setups.
This vision kept us grounded as we experimented with different methods.
Methods We Tried
1. Pandas
- Pros:
- Widely known and very easy to use.
- Great for loading simple tables into DataFrames.
- Cons:
- Could not detect native Excel tables.
- Required heavy custom table-boundary logic.
- Failed to capture surrounding context.
Verdict: Solid for basic jobs but not enough for complex parsing.
2. OpenPyXL
- Pros:
- Reads native Excel tables and cell text.
- Cons:
- Missed simple tabular ranges.
- Still demanded extra parsing logic to unify outputs.
Verdict: A step up from Pandas, but still incomplete.
3. LlamaIndex
- Pros:
- Provides an end-to-end pipeline: parsing + querying.
- Cons:
- Required two API keys (Llama Parse + OpenAI).
- Depended on paid APIs, against our free/local requirement.
Verdict: Too costly and external for our workflow.
4. Marker
- Pros:
- Offered both LLM-powered and non-LLM modes.
- The LLM version delivered impressive parsing results.
- Cons:
- LLM mode consumed too many OpenAI tokens, driving up costs.
- Non-LLM mode often hallucinated tags and produced errors.
- Required significant post-processing.
Verdict: Interesting experiment, but unstable and costly.
5. Docling (Final Choice)
- Pros:
- Strong parsing engine capable of handling tables + text.
- Multiple export options: Dict, HTML, Text, Element Nodes, and more.
- Local-first, no reliance on external APIs.
- Cons:
- Export formats each had small quirks.
- Solution:
- We standardized on the
dictexport for flexibility. - Added custom logic to handle quirks and standardize outputs.
- We standardized on the
Verdict: Flexible, scalable, and powerful enough for production.
Example Applications
Docling can be applied in real-world scenarios such as:
- Financial reporting: Parsing monthly Excel reports into structured data for automated dashboards.
- Survey analysis: Extracting tabular responses along with explanatory notes for research insights.
- Operational logs: Capturing tables from Excel logs while retaining context from comments and footnotes.
- Data migration: Converting legacy Excel-based datasets into standardized formats for new systems.
- Compliance audits: Extracting both tables and supporting text from Excel-based audit reports for validation.
Business Impact
Switching to Docling delivered clear results:
- 50–70% reduction in engineering effort: Developers no longer needed to maintain complex parsing logic.
- Higher accuracy: Tables and surrounding notes were consistently extracted, reducing manual corrections.
- Cost savings: Avoiding paid APIs removed recurring expenses.
- Significant time savings: For example, processing a batch of 500 Excel reports that previously required multiple analysts now takes a few hours on a single machine.
- Improved decision-making: Teams gained quicker access to accurate, structured data for reporting and analysis.
Performance Results
We also measured Docling’s performance against our needs:
Test Case 1 – Cell values as strings
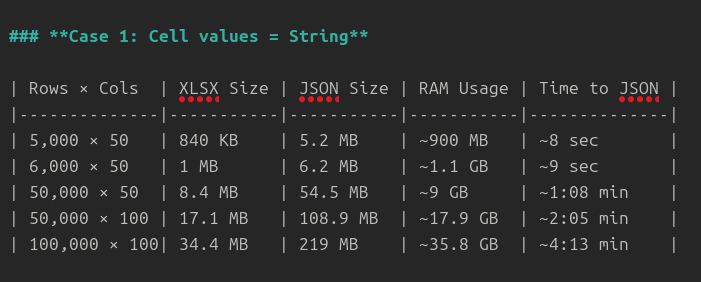
Test Case 2 – Cell values as floats

Conclusion
Parsing Excel at scale is harder than it looks, most tools solve one piece of the puzzle but fall short elsewhere. Through trial and error, we found Docling to be the most complete and reliable solution, balancing accuracy, scalability, and flexibility.
By adopting Docling, organizations can streamline their data workflows, reduce costs, and unlock more value from Excel-based information at scale.

Contact Us
Let’s Build Your Digital Success Story
With decades of expertise and hundreds of future-ready solutions delivered globally, GiganTech combines technical mastery and industry insights to turn complex challenges into growth. Partner with a team trusted by enterprises worldwide—where technology meets innovation.


